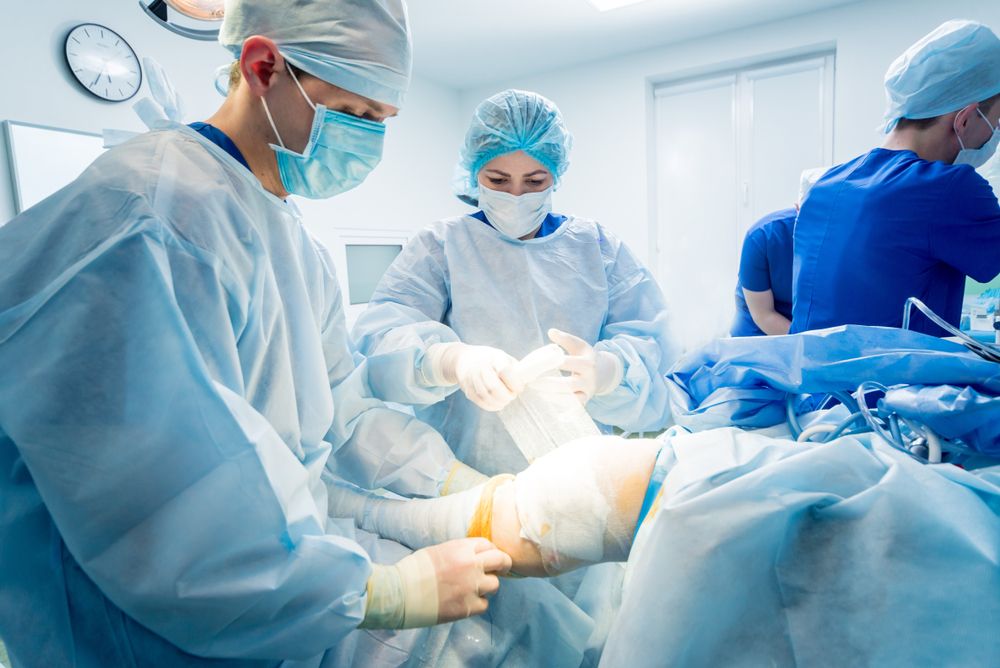
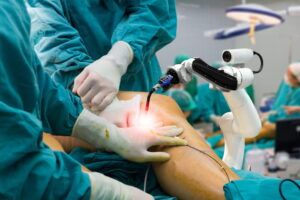
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat joint issues with precision and less recovery time compared to traditional open surgeries. At Premier Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine, P.C., serving patients in Bloomfield, Englewood, and Union City, NJ, this advanced surgical option offers a way to address common joint problems without the extensive downtime associated with more invasive procedures. In this blog, we’ll cover key insights into arthroscopic surgery, including what it is, how it works, and what you can expect during recovery.
What Is Arthroscopic Surgery?
Arthroscopic surgery is a technique that allows surgeons to look inside a joint using a small camera, called an arthroscope, and perform repairs or other procedures through tiny incisions. Unlike open surgery, which requires large cuts, arthroscopy uses only a few small incisions, reducing trauma to the surrounding tissues and promoting faster recovery.
The arthroscope is connected to a video monitor, giving the surgeon a clear view of the joint’s interior. Surgical tools are then inserted through additional small incisions to treat issues such as torn ligaments, cartilage damage, or loose bone fragments.
Common Joints for Arthroscopic Surgery
While arthroscopic surgery can be used for many joints, the most common areas include:
- Knee: For meniscus tears, ligament repairs, and cartilage trimming.
- Shoulder: To treat rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, and instability.
- Ankle: For addressing ligament injuries, scar tissue, and cartilage defects.
- Elbow: Often used for tennis elbow or removing loose bodies.
- Hip: To address labral tears, impingement, or cartilage issues.
Benefits of Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery has several benefits over traditional open surgery, which is why it’s a preferred method for many patients dealing with joint issues.
- Minimally Invasive: The small incisions used in arthroscopy cause less damage to the surrounding muscles and tissues compared to open surgery. This means less pain and discomfort after surgery, which translates to a faster recovery and less need for pain medication.
- Shorter Recovery Time: With less tissue trauma, patients typically experience a quicker return to normal activities. Most arthroscopic surgeries are outpatient procedures, meaning you can go home the same day, and in many cases, patients can return to work and light activities within a few days to a week.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions also lower the risk of infection, which is always a concern in any surgical procedure. The less invasive nature of arthroscopy minimizes exposure, reducing complications associated with larger, more invasive procedures.
- Precision and Clarity: The high-resolution camera used in arthroscopic surgery provides a clear, magnified view of the joint, allowing the surgeon to identify and treat even minor issues that might not be visible with traditional surgical techniques. This precision leads to better outcomes and fewer post-surgical complications.
Conditions Treated with Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery can be used to treat a wide range of joint conditions. Some of the most common include:
- Meniscus Tears: Meniscus tears are among the most frequent knee injuries and are particularly common in athletes. Arthroscopy allows the surgeon to trim or repair the damaged cartilage with minimal disruption to the surrounding tissue.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Rotator cuff injuries, often caused by repetitive shoulder movements or trauma, can lead to significant pain and limited mobility. Arthroscopic surgery can repair these tears and alleviate discomfort, restoring function to the shoulder.
- ACL Reconstruction: Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries in the knee are common among athletes involved in high-impact sports. Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction involves replacing the damaged ligament with a graft, allowing for faster recovery and improved stability.
- Joint Debridement: In cases where loose fragments of bone or cartilage are present within a joint, arthroscopy can be used to remove these fragments, which can reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Synovectomy: For patients with chronic inflammation of the joint lining (synovium), such as in rheumatoid arthritis, arthroscopic surgery can remove the inflamed tissue, relieving pain and improving mobility.
The Arthroscopic Surgery Process
Understanding what to expect during the arthroscopic surgery process can help reduce any anxiety and ensure a smoother experience. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Preoperative Consultation
Before the surgery, you will meet with your orthopedic surgeon to discuss the procedure in detail. This consultation will include a physical examination, imaging tests, and a review of your medical history. Your surgeon will explain the specific issues within your joint and how arthroscopy can address them.
2. Day of Surgery
On the day of your surgery, you will arrive at the surgical center or hospital for preoperative preparation. Depending on your procedure, you may be given either local, regional, or general anesthesia. The surgeon will make small incisions near the joint and insert the arthroscope to view the joint’s interior. Any necessary repairs or treatments will be carried out using specialized tools.
3. Post-Surgery Recovery
After the procedure, you will be taken to a recovery room to be monitored for a short time. Most patients are able to go home the same day. You’ll be given specific instructions regarding care for the surgical site, activity limitations, and follow-up appointments. Physical therapy is often prescribed to aid in rehabilitation and ensure the best possible recovery.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery time for arthroscopic surgery varies depending on the joint treated and the specific procedure performed. However, one of the major advantages of arthroscopy is the relatively short recovery period compared to traditional surgeries.
Immediate Recovery
In the first few days following surgery, it is essential to rest the joint and follow your doctor’s instructions regarding weight-bearing or movement restrictions. Icing the joint and elevating it can help reduce swelling. Pain medication may also be prescribed to manage any post-surgical discomfort.
Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is typically a key part of recovery. Your physical therapist will guide you through exercises designed to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected joint. The sooner you start physical therapy, the better your chances of a full recovery.
Moving Forward After Arthroscopy
Arthroscopic surgery is a valuable tool for addressing a variety of joint problems with minimal disruption to a patient’s life. Its minimally invasive nature, precision, and faster recovery make it a preferred option for many patients. Whether it’s knee pain, a shoulder injury, or another joint issue, the orthopedic specialists at Premier Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine, P.C. are here to provide expert care.
If you are considering arthroscopic surgery or have questions about whether it’s the right option for you, our team is available for consultations at our locations in Bloomfield, Englewood, and Union City, NJ. We will work with you to determine the best course of action based on your individual needs and circumstances.
Sources:
- Sherman, O. H., & Fox, J. M. (2013). The Evolution of Arthroscopic Surgery. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery.
- Cole, B. J., & Sekiya, J. K. (2014). Surgical Techniques for Arthroscopic Shoulder Repair. The Lancet.
- Rodeo, S. A. (2017). Advances in Arthroscopic Surgery: New Frontiers. Orthopedic Clinics of North America.